Industries in which Ion/Plasma Nitriding is Implemented
Many parts and tools of all industries are subject to plasma nitriding and ferritic nitrocarburising. Different examples demonstrate how plasma nitriding and nitrocarburising solve tough tasks.
Here are some examples of industries where they are applied:
Automobile Industry - crankshafts, camshafts, gears, pistons, cylinders, valves, valve springs, synchromesh rings;
Metal Casting and Moulding Industries - moulds for non-ferrous metals and alloys;
Forging Industry - all kinds of dies for hammering and pressing (cold forging, impression forging, open die forging);
Aluminium Industry - dies for casting and extruding;
Plastics Industry - extruder screws, cylinders, moulds for injection moulding;
Machine Building - shafts, spindles, slide-rails, instruments for cold and hot rolling, dies and punches for deep drawing, pump cylinders, milling and drilling tools (milling cutters, rams, drills, taps, broaches, etc.);
Powder Metallurgy - gears, bushes, synchromesh rings;
Power Engineering - turbines, shafts, spindles, gears.
Results after Ion/Plasma Nitriding
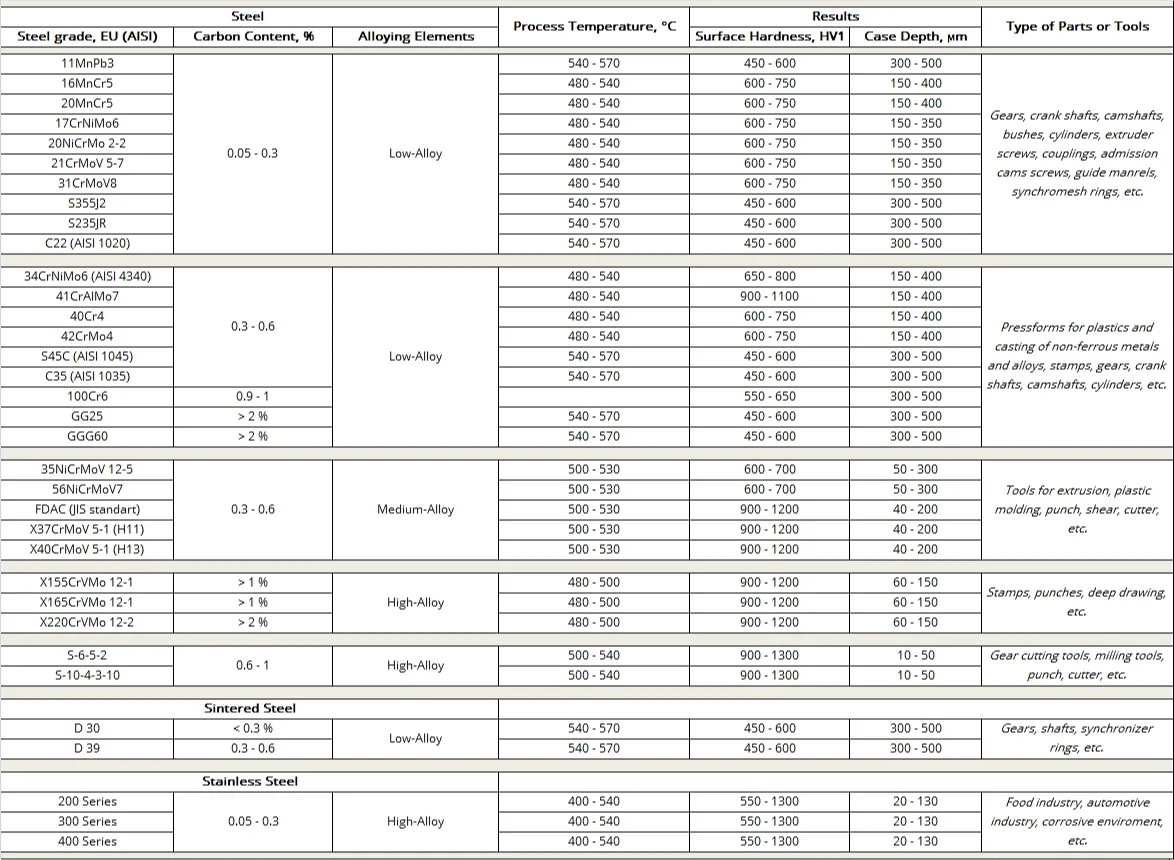
These are some of the possible steel grades for Plasma Nitriding and Nitrocarburising. For information about other steel grades and results, please, do not hesitate to contact us at: office@ionitech.com
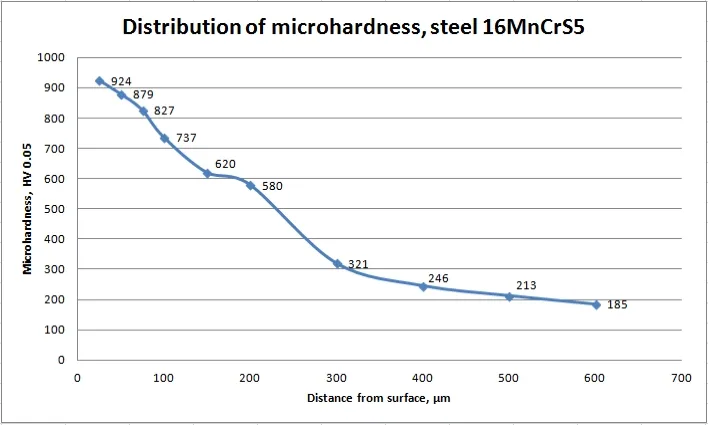
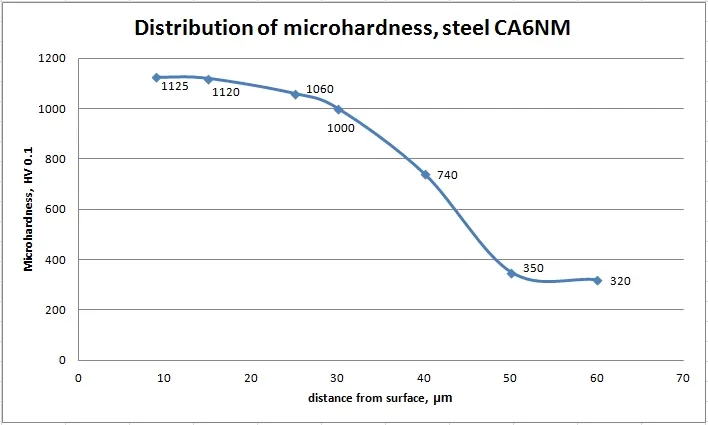
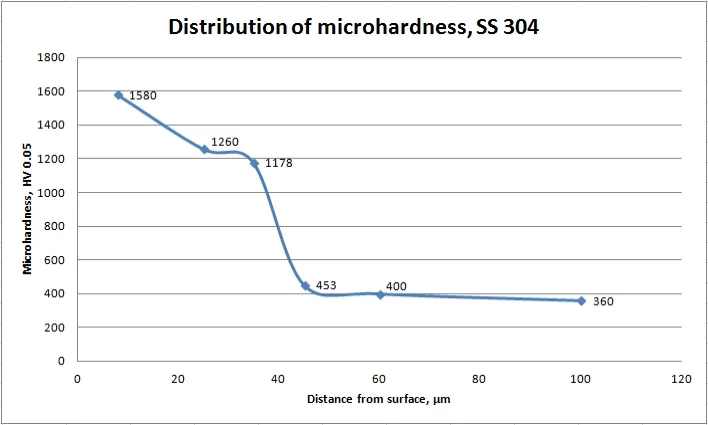
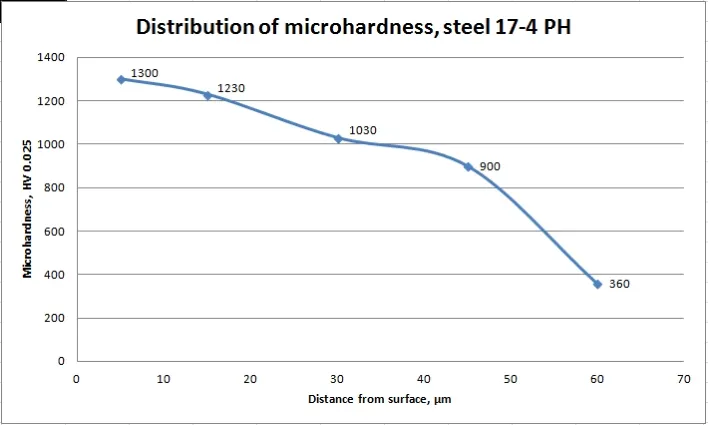
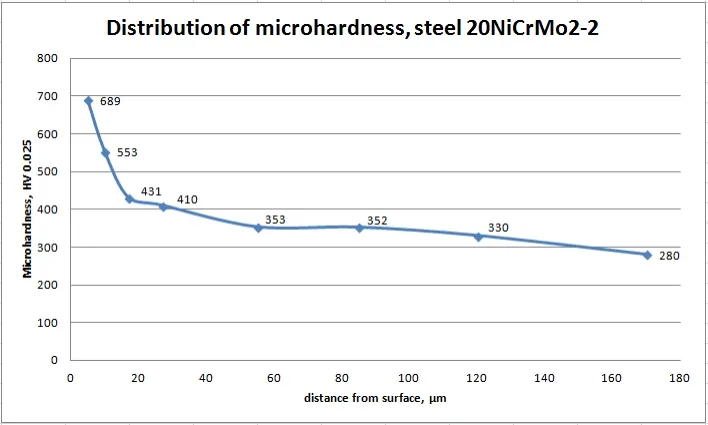
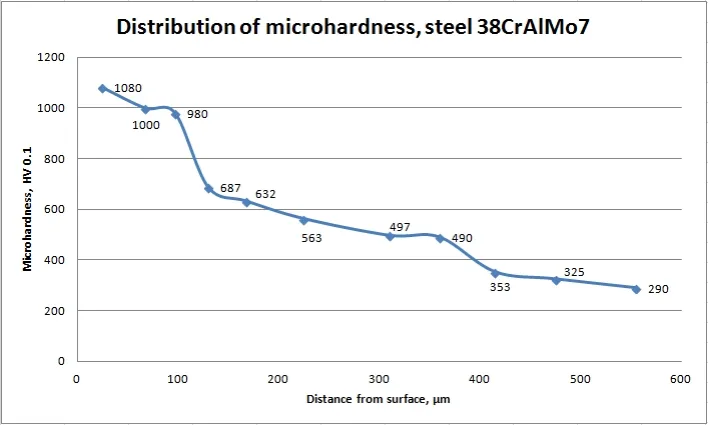
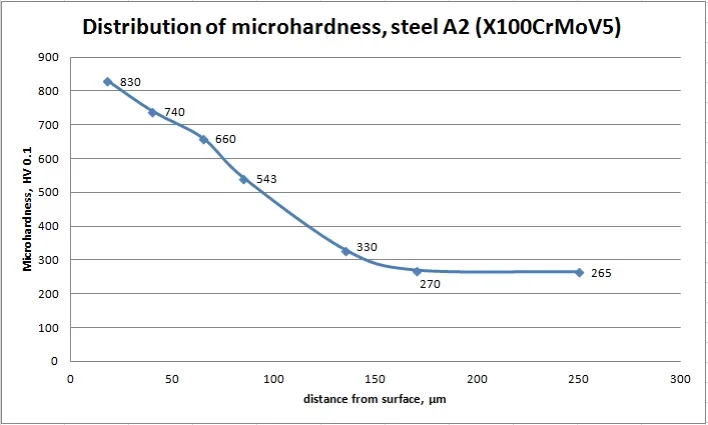
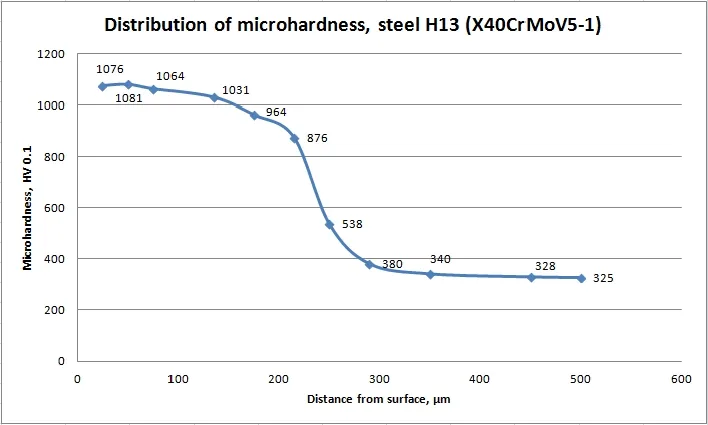
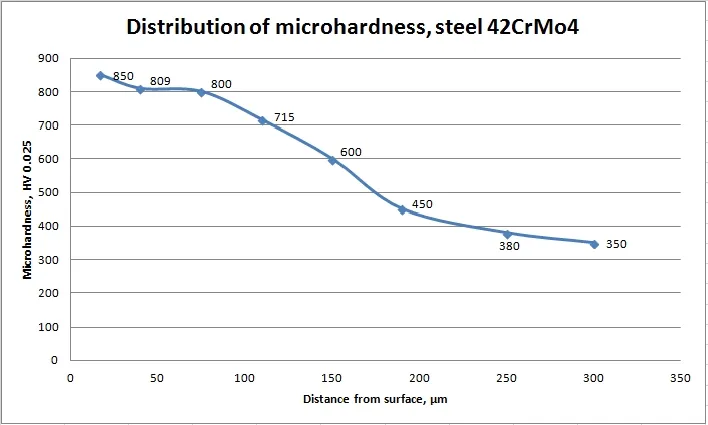
Microhardness in depth of nitrided steels
The depth of the diffusion of nitrogen in the steel depends on the Plasma Nitriding Process parameters.
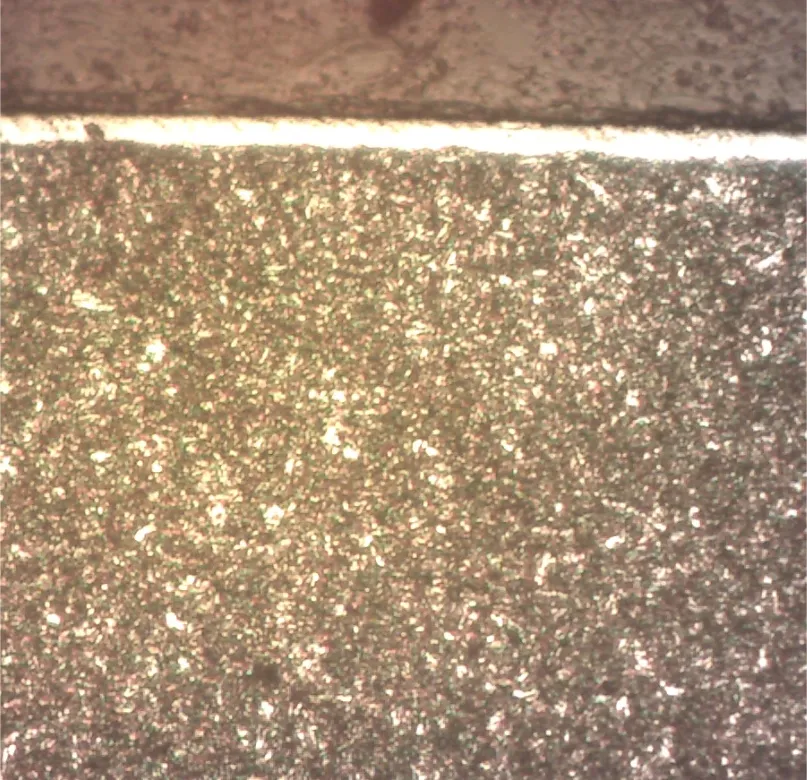
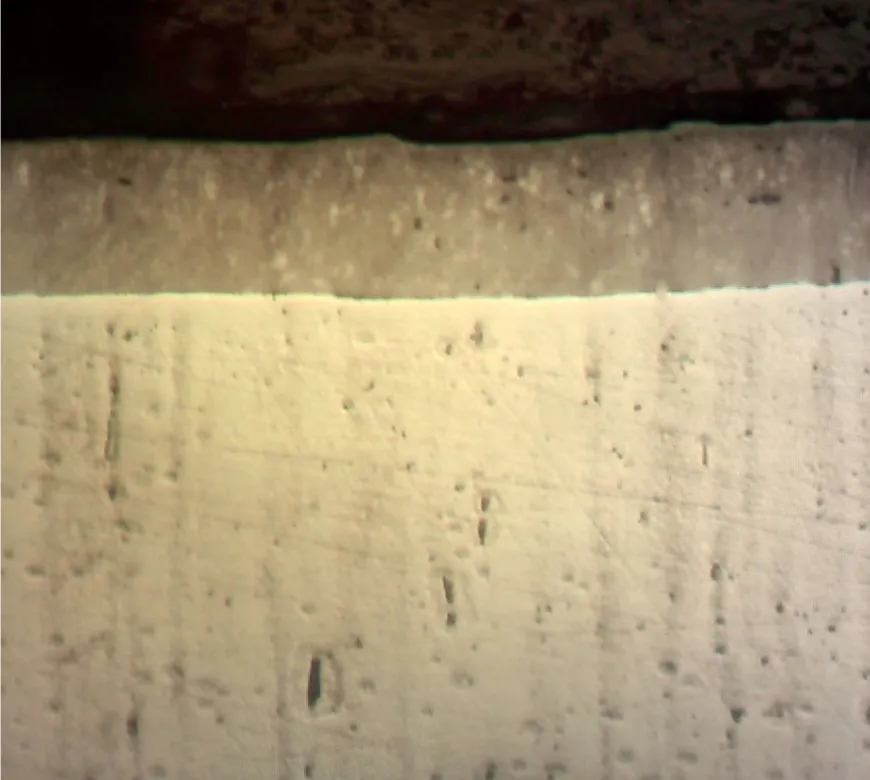
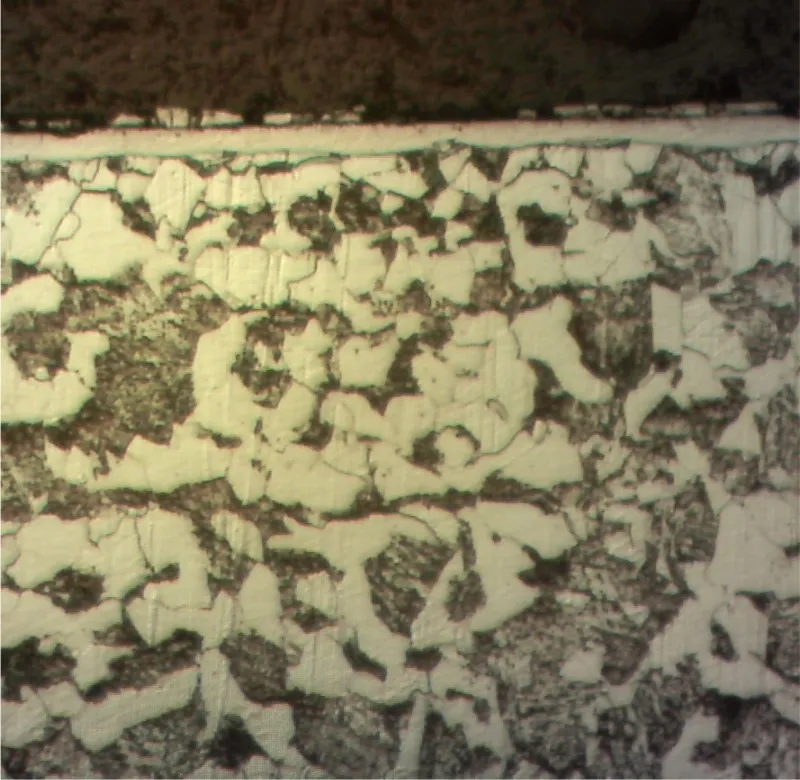
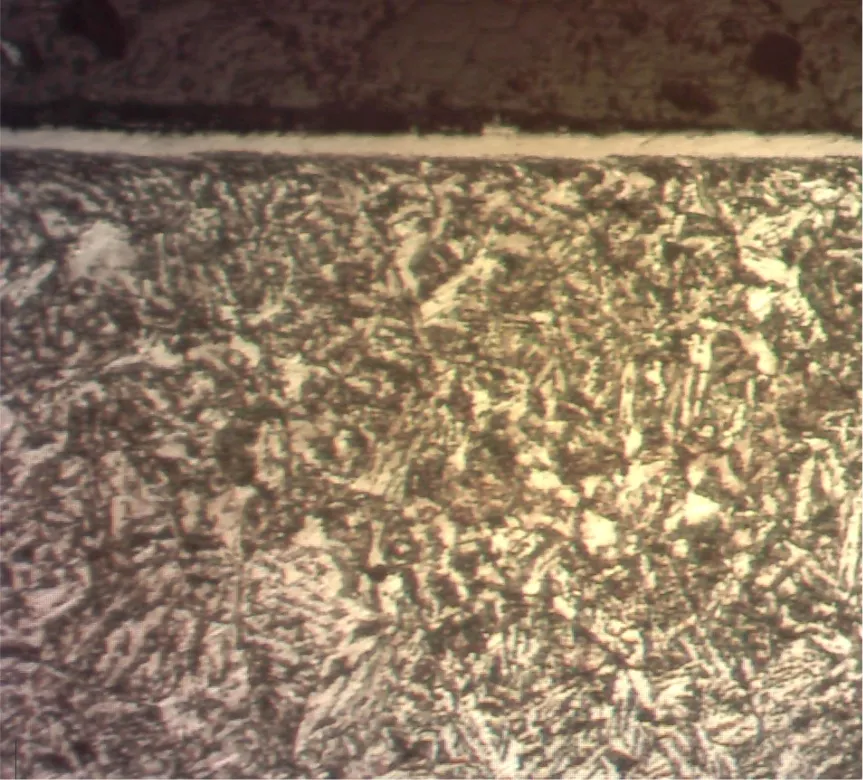
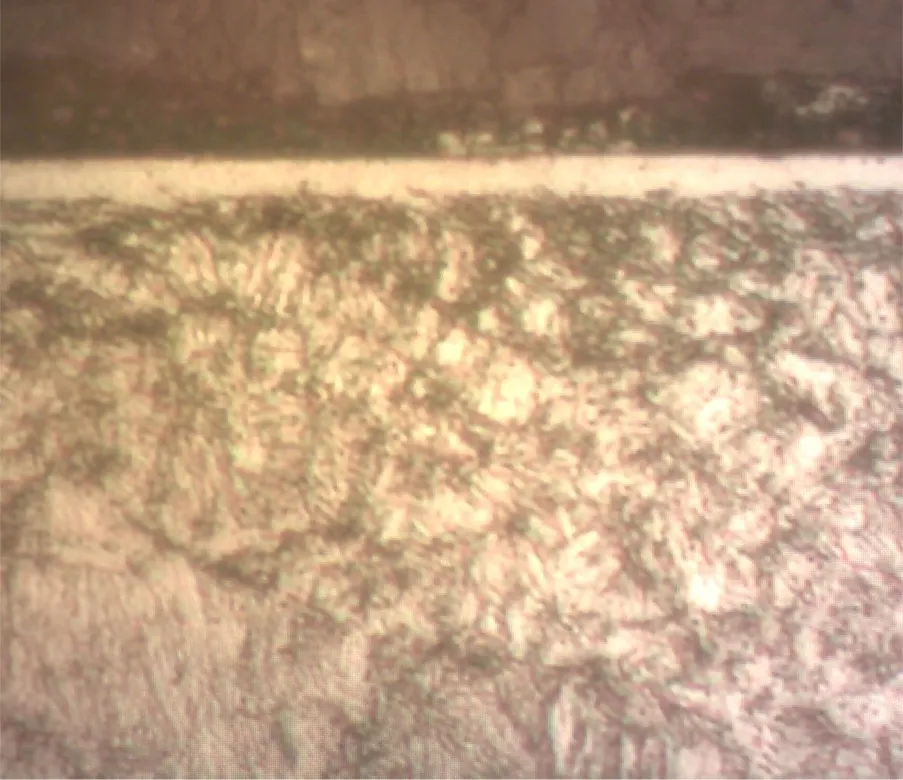
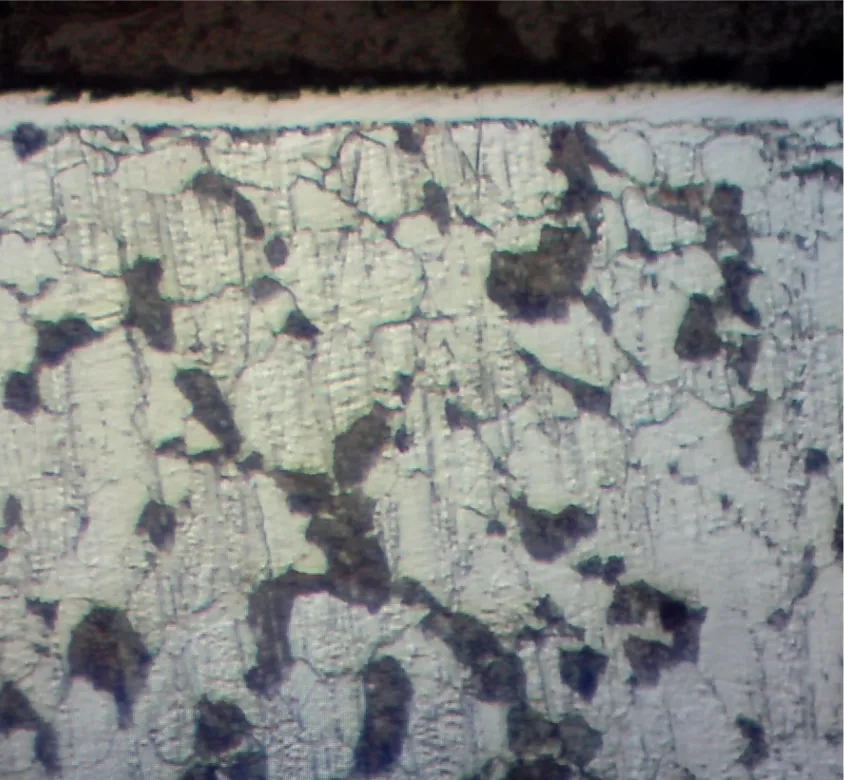
Metallographic images of Compound (White) Layer and diffusion zone
The thickness of the compound (white) layer and the depth of the diffusion zone could be controlled by the Plasma Nitriding Process parameters.
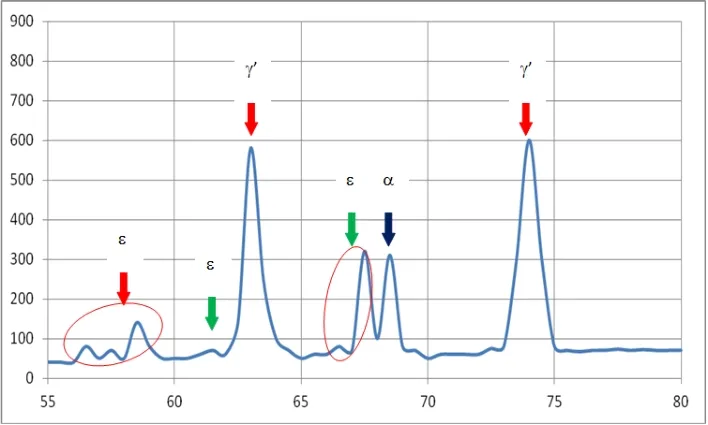
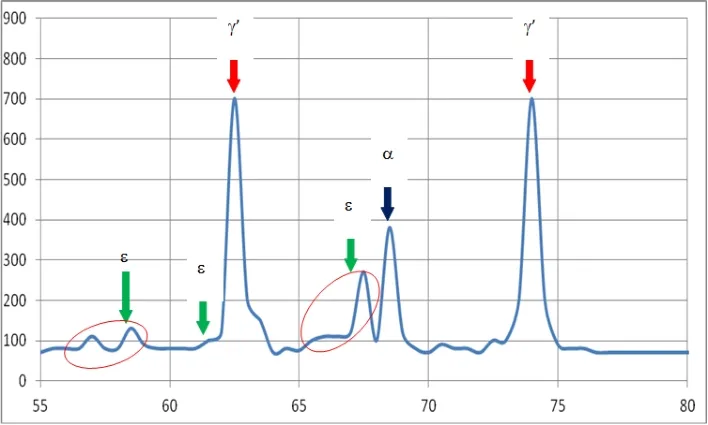
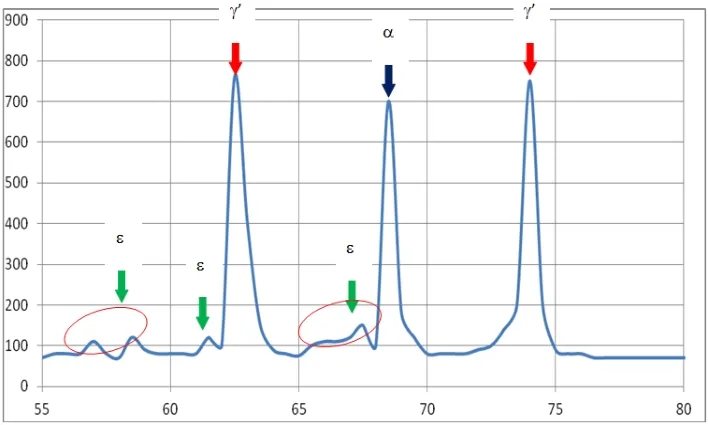
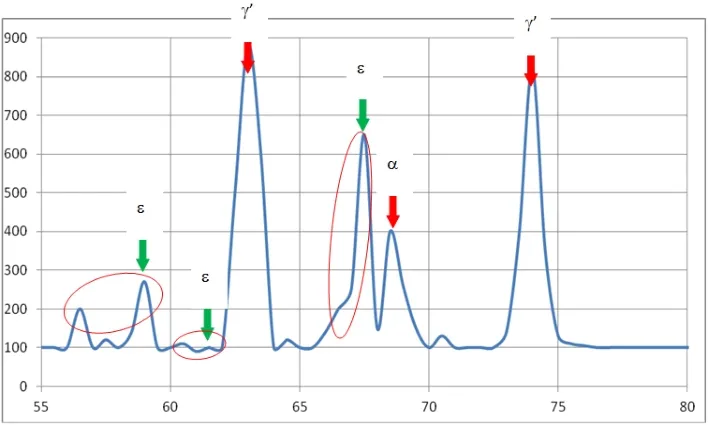
Phase structure of Compound Layer
By regulating the gaseous phase composition and the pulse glowing discharge parameters diffusion layer with monophase-γ'-zone (Fe4N), with monophase-ε-nitride zone (Fe2-3N) or nitrided layers without any nitride zone can be obtained. The achieved nitride zones are dense and solidly connected with the base metal.



 English (United Kingdom)
English (United Kingdom)  Русский (Россия)
Русский (Россия)  Български (България)
Български (България)  Español (España)
Español (España)